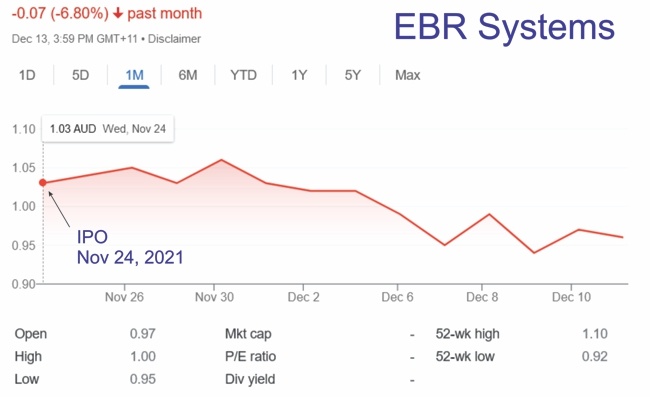
Image Credit: Fire 1
FIRE1 is an Ireland-based company developing an implantable Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) size sensor for heart failure monitoring. The FIRE1 System is a device designed to directly measure a patient’s volume status by measuring the IVC, which is the largest vein in the body where most fluid is stored.
The FIRE1 sensor is implanted at the abdominal level and works by measuring the size of the IVC to give a marker of the amount of fluid in the body. High levels can increase the risk of breathing difficulties and a build-up of fluid in the lungs which lead to an emergency hospital admission. The patient wears a belt reader around the abdomen for around a minute a day to take a reading from the sensor and the data is sent to the patient’s clinical team at the hospital. The system is designed to alert whenever the patient’s condition deteriorates.
In March 2024, FIRE1 announced that it has completed patient enrollment in the U.S. Early Feasibility Study (FUTURE-HF2) of its system. Results presented at CRF’s THT showed that all enrolled patients (n=8) met their safety and effectiveness endpoints.


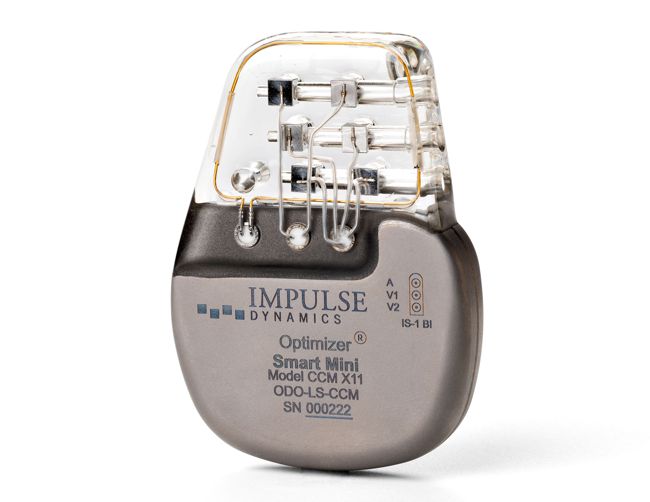
 Impulse Dynamics, the company where I’m CTO and Executive VP,
Impulse Dynamics, the company where I’m CTO and Executive VP,