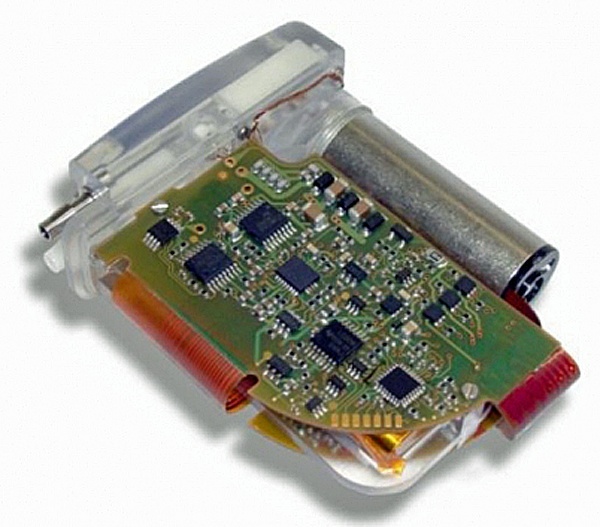
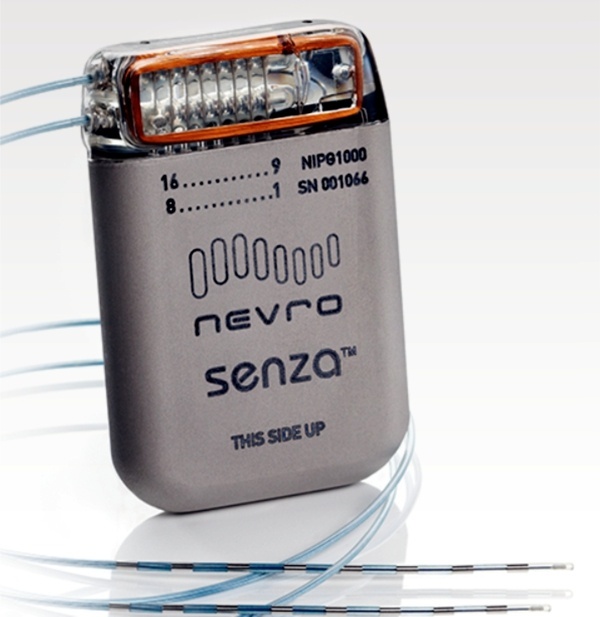
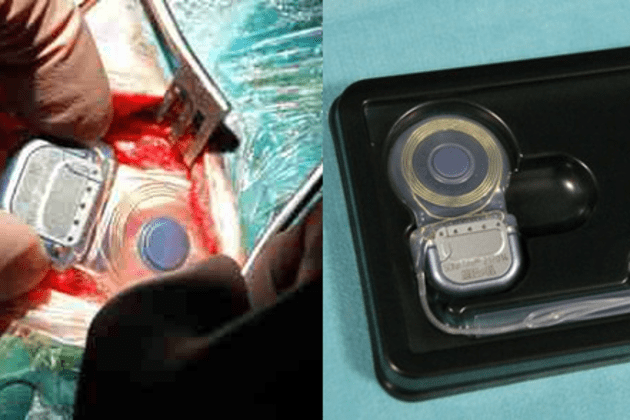
Toronto-based Functional Neuromodulation announced that it implanted the first U.S. Alzheimer’s patient in the “ADvance Study” with a deep brain stimulation (DBS) system meant to improve cognitive performance. ADvance will evaluate the safety and potential clinical benefit of DBS of the fornix (DBS-f), a major inflow and output pathway in the brain’s memory circuit, for patients with mild Alzheimer’s. The ADvance Study is being conducted using Medtronic Activa DBS IPGs.
Toronto-based Functional Neuromodulation announced that it implanted the first U.S. Alzheimer’s patient in the “ADvance Study” with a deep brain stimulation (DBS) system meant to improve cognitive performance. ADvance will evaluate the safety and potential clinical benefit of DBS of the fornix (DBS-f), a major inflow and output pathway in the brain’s memory circuit, for patients with mild Alzheimer’s. The ADvance Study is being conducted using Medtronic Activa DBS IPGs.
While DBS has been an effective treatment for movement disorders for more than 15 years, it was only recently that this approach was first applied to Alzheimer’s. Dr. Andres Lozano, a neurosurgeon at University of Toronto and Scientific Founder of Functional Neuromodulation, originated the concept of treating memory disorders using deep brain stimulation (DBS) while treating a patient suffering from morbid obesity. In this patient, DBS stimulation of the hypothalamus and fornix was associated with an unexpected observed improvement in the patient’s memory.


 I received today a
I received today a  Biotronik announced the European market release of BioMonitor®, an implantable cardiac device designed for the highly accurate and reliable monitoring and management of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) or unexplained syncope.
Biotronik announced the European market release of BioMonitor®, an implantable cardiac device designed for the highly accurate and reliable monitoring and management of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) or unexplained syncope.
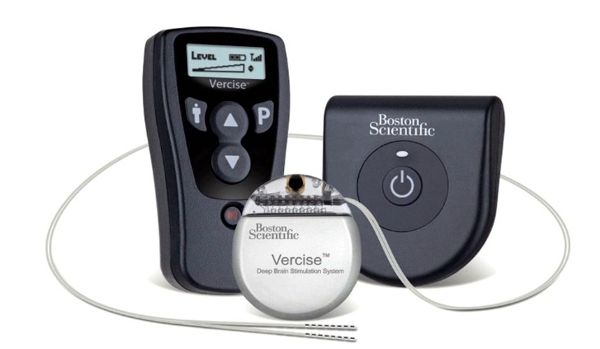


 St. Jude Medical announced it has received European CE Mark approval of its Eon™ family of neurostimulators for treating patients with intractable chronic migraine.
St. Jude Medical announced it has received European CE Mark approval of its Eon™ family of neurostimulators for treating patients with intractable chronic migraine.