
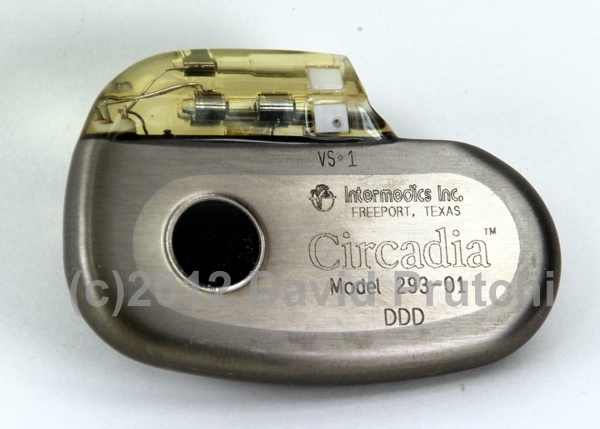
I took this picture a very long time ago at the office of one of my implanter friends in Europe. Ever since then, I’ve tried to find out about “Digikon,” but have had no luck so far. All that I have been able to find from the St. Jude legacy device database is that Digikon had produced a number of pacemaker models, including the one shown in this picture.



 One of the indicators of metabolic demand that has been used for controlling the rate of pacemakers is central venous blood temperature (CVT).
One of the indicators of metabolic demand that has been used for controlling the rate of pacemakers is central venous blood temperature (CVT).

 Leptos Biomedical was founded in Fridley, MN in 2002 by Dr. John D. Dobak. Leptos intended to develop an implantable device to stimulate the greater splanchnic nerve, that was hoped would result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure.
Leptos Biomedical was founded in Fridley, MN in 2002 by Dr. John D. Dobak. Leptos intended to develop an implantable device to stimulate the greater splanchnic nerve, that was hoped would result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure.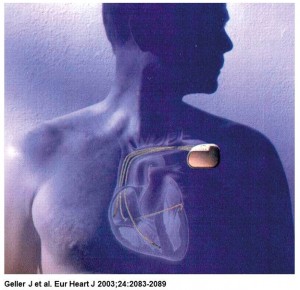 InControl was founded in 1990 in Redmond, WA to develop an implantable device for treating atrial fibrillation. In November 1995, InControl announced the first human implant of its Metrix atrioverter.
InControl was founded in 1990 in Redmond, WA to develop an implantable device for treating atrial fibrillation. In November 1995, InControl announced the first human implant of its Metrix atrioverter.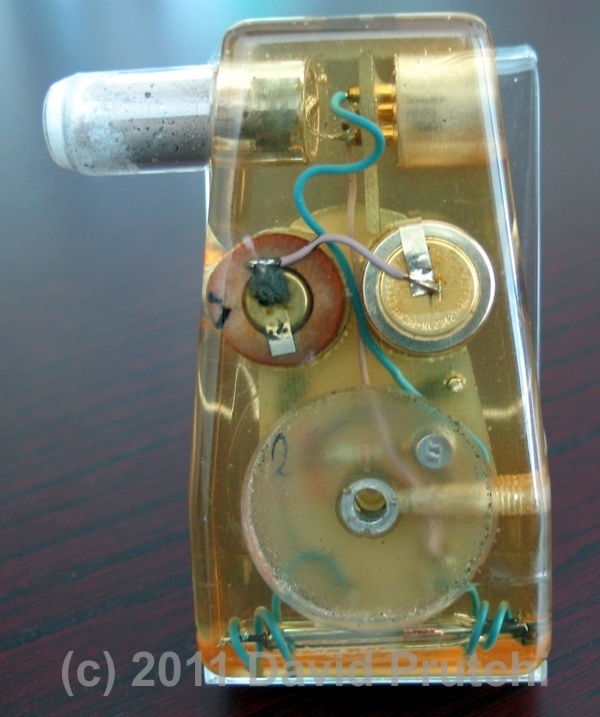
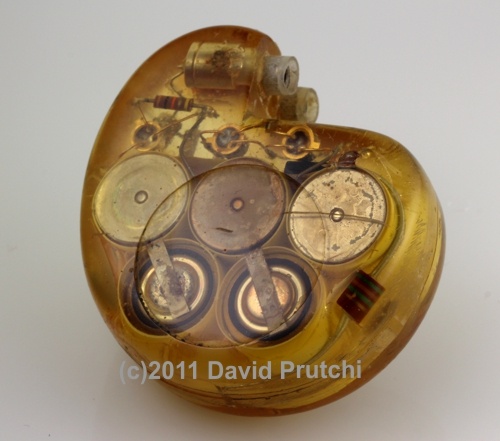
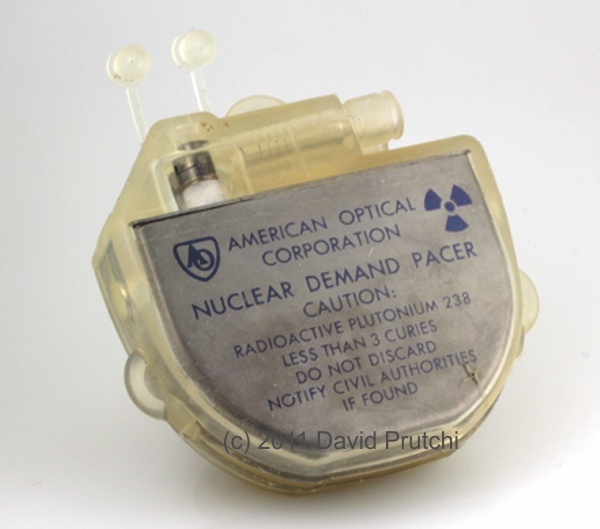


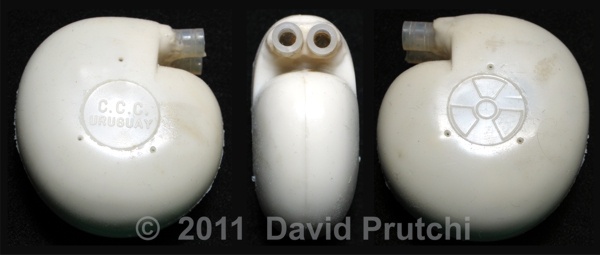


 CCC is one of the oldest pacemaker manufacturers in the world. It was founded in 1969 by Dr. Orestes Fiandra, who performed the first succesful, human, long-term pacemaker implant in the world.
CCC is one of the oldest pacemaker manufacturers in the world. It was founded in 1969 by Dr. Orestes Fiandra, who performed the first succesful, human, long-term pacemaker implant in the world.