St. Jude Medical today reported sales and net earnings for the first quarter ended March 31, 2012.
St. Jude Medical today reported sales and net earnings for the first quarter ended March 31, 2012.
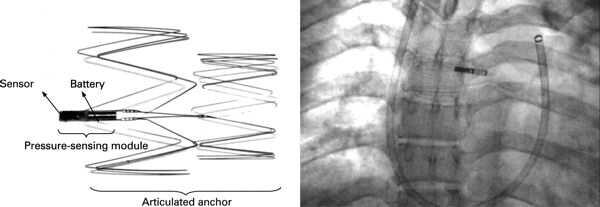
Total CRM sales, which include ICD and pacemaker products, were $735 million for the first quarter of 2012, a 4 percent decrease compared with the first quarter of 2011. Of that total, ICD product sales were $450 million in the first quarter, a 3 percent decrease compared with the first quarter of 2011. First quarter pacemaker sales were $285 million, a decrease of 4 percent from the comparable quarter of 2011.
St. Jude Medical sales of neuromodulation products were $103 million in the first quarter of 2012, up 12 percent from the comparable quarter of 2011.
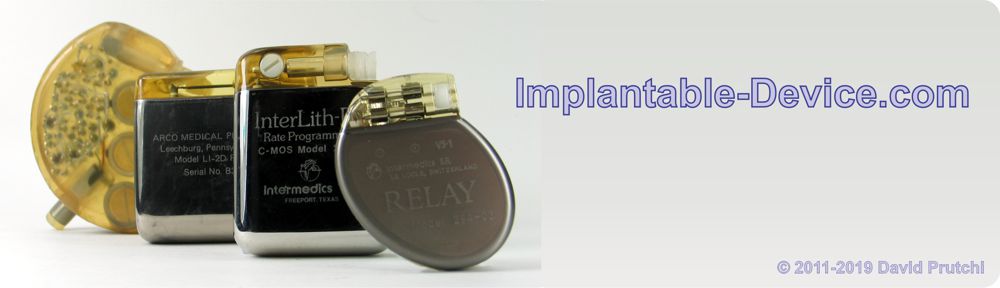





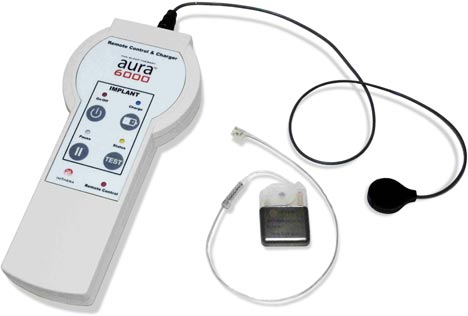

 In 1965, Australian medical device pioneer Noel Gray established Telectronics – Australia’s first manufacturing facility for producing pacemakers that were designed in-house. Telectronics was an innovative developer, achieving some major successes in the early cardiac pacing field, for example, Telectronics’ leads allowed narrowing the pacing pulse to its current nominal of 0.5 milliseconds; encapsulating the pacemaker in titanium instead of epoxy; using a microplasma weld to join the two halves of the pacemaker capsule; creating one of the first rate-responsive ‘demand’ pacemakers; and isolating the pacemaker’s battery in a separate compartment to deal with the problem of leaking mercury-zinc batteries.
In 1965, Australian medical device pioneer Noel Gray established Telectronics – Australia’s first manufacturing facility for producing pacemakers that were designed in-house. Telectronics was an innovative developer, achieving some major successes in the early cardiac pacing field, for example, Telectronics’ leads allowed narrowing the pacing pulse to its current nominal of 0.5 milliseconds; encapsulating the pacemaker in titanium instead of epoxy; using a microplasma weld to join the two halves of the pacemaker capsule; creating one of the first rate-responsive ‘demand’ pacemakers; and isolating the pacemaker’s battery in a separate compartment to deal with the problem of leaking mercury-zinc batteries.